Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is the inflammation of the upper genital tract and its surrounding tissues, and includes disorders such as endometritis, tuboovarian abscess and pelvic peritonitis. PID can be divided into chronic and acute types. The main symptoms of acute PID include fever, increased vaginal fluids and constant lower abdominal pain that is aggravated by physical activity or sexual intercourse. In serious cases, there can be chills, high fever, headache and poor appetite. Chronic PID can arise from acute PID that was not completely cured, or because of a weak constitution. The manifestations of chronic PID include lower abdominal pain and heaviness, and aching pain of the lumbosacral region, both of which are aggravated with physical activity, sexual intercourse, and before or after menstruation.
In TCM, PID falls under abnormal vaginal discharge, as well as concretions and conglomerations. The disease usually involves one or more of five disease mechanisms. First, it can be caused by damp-heat that arises when spleen deficiency or eating too much rich food allows damp to accumulate. Second, it can be the result of damp-heat pouring downward due to a combination of liver heat, spleen dampness and liver constraint. Third, it can be caused by living in a damp environment for long periods, excessive sexual activity,or damp-heat attacking the lesser abdomen (the lateral parts of the lower abdomen). Fourth, it can be due to an excess of damp-cold that has accumulated due to yang deficiency, or dampcold attacking the uterus and lesser abdomen. Fifth, PID can arise from blocked qi movement due to mental depression, or qi stagnation and blood stasis in the uterus caused by surgery.PID most often involves damp-heat, damp-cold or stasis in the lesser abdomen and uterus, which affects the Chong mai and Ren mai.
Clinical manifestations of PID
- Abdominal pain, lower back pain, and an uncomfortable feeling of heaviness around the anus, all of which can be aggravated by physical activity, sexual intercourse, defecation, or before or after the menstrual period. There can also be a fever in the acute stage.
- The above symptoms can be accompanied by a variety of menstrual disorders, such as increased menstruation, irregular vaginal bleeding and dysmenorrhea.
- Abnormal color or volume of vaginal discharge.
6 Acupuncture points for PID
The basic therapeutic principles are to clear heat, drain dampness, invigorate blood and dissolve stasis. Relevant acupoints are chosen according to the following principles: the kidney is in charge of reproduction; the liver governs the free flow of qi; the spleen governs the transportation and transformation of water-dampness; the Chong Mai and Ren Mai govern the menses.
1. GV 3 Acupoint (Yaoyangguan)
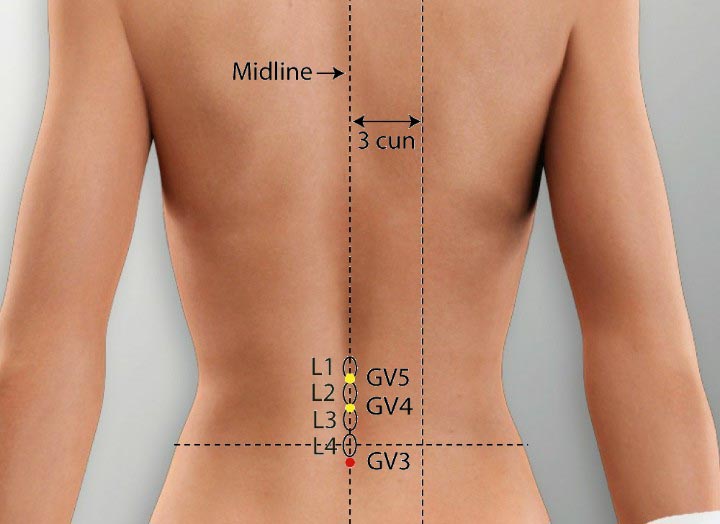
Location: On the posterior midline in the depression below the spinous process of the fourth lumbar vertebra.
Effect: Supplements the kidney, regulates menstruation, dissipates cold, relieves pain.
2. BL 32 Acupoint (Ciliao)
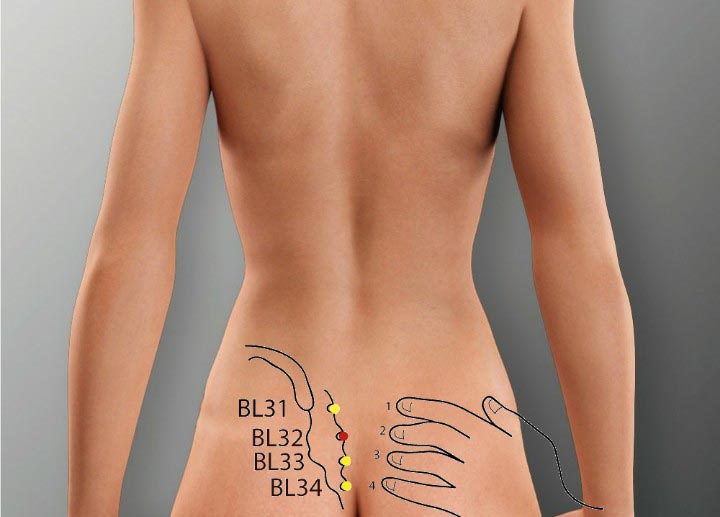
Location: On the medial-inferior side of the posterior inferior iliac spine, over the second posterior sacral foramina.
Effect: Rectifies qi, and regulates menstruation.
3. CV 4 Acupoint (Guanyuan)
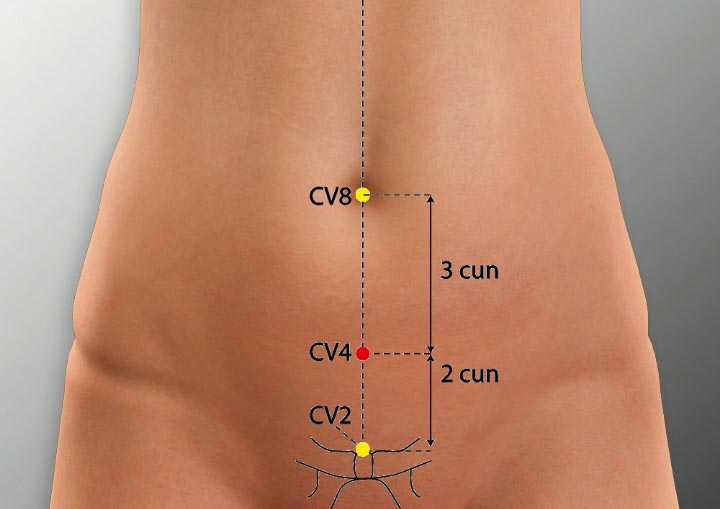
Location: On the lower abdomen on the anterior midline, 3 cun below the umbilicus.
Effect: Warms and supplements original yang, regulates menstruation.
4. EX-CA1 Acupoint (Zigong)
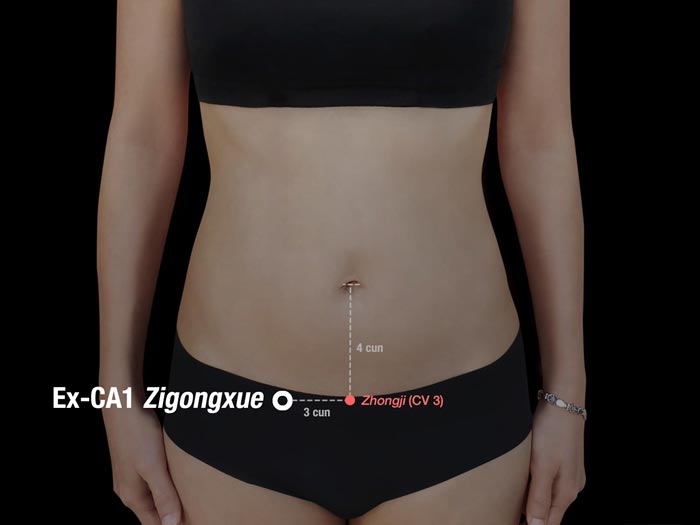
Location: On the lower abdomen 4 cun below the umbilicus, 3 cun lateral to CV 3.
Effect: Regulates menstruation, relieves pain.
5. SP 6 Acupoint (Sanyinjiao)
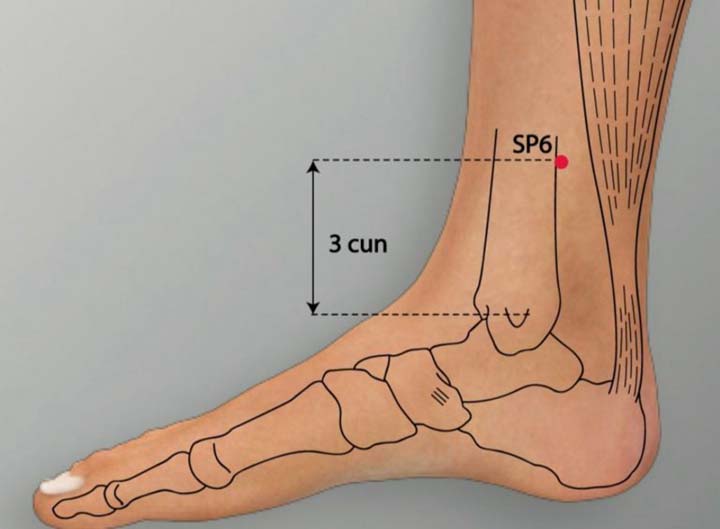
Location: On the medial lower leg 3 cun above the medial malleolus, in the depression posterior to the medial border of the tibia.
Effect: Regulates blood, supplements yin, dispels stasis and relieves pain.
6. SP 9 Acupoint (Yinlingquan)
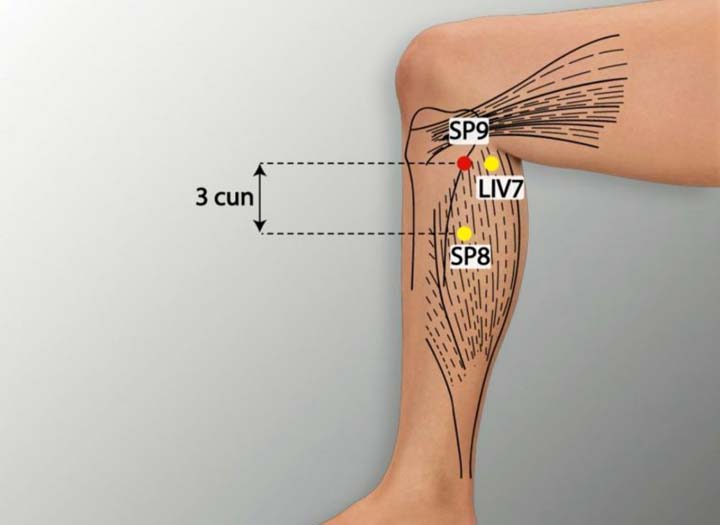
Location: On the medial leg, in the depression posterior and inferior to the medial condyle of the tibia.
Effect: Fortifies the spleen, removes dampness, regulates menstruation.
Moxibustion treatment methods
- Mild moxibustion on GV 3 and BL 32. The patient should feel the heat penetrating deep into the abdomen, or expanding over the lumbosacral region or lower extremities. Located on the Du Mai, GV 3 can supplement the kidney, regulate menstruation, dissipate cold and relieve pain. Located on the foot taiyang bladder channel, BL 32 rectifies qi and regulates menstruation.
- Mild moxibustion on CV 4 and EX-CA1. The patient should feel the heat penetrating deeply into the abdominal cavity. Both CV 4 and EX-CA1 are located in the lower jiao, and use together can warm and supplement the original yang, regulate menstruation and relieve pain.
- Double-point mild moxibustion on SP 6. In some patients, the heat will reach the abdomen. If it fails to do so, administer relaying moxibustion with another moxa stick on the most proximal place the heat has reached to cause the heat to transmit to the abdomen. Finally, administer mild moxibustion on bilateral SP 6 and the abdomen until the heat-sensitive sensation disappears. SP 6 is an intersecting point of the three yin channels of the foot, and can regulate blood, supplement yin, dispel stasis and relieve pain.
- Double-point mild moxibustion on SP 9. In some patients, the heat will reach the abdomen. If it fails to do so, administer relaying moxibustion with another moxa stick to the most proximal place the heat has reached to cause the heat to transmit to the abdomen. Finally, administer mild moxibustion on SP 9 and the abdomen until the heat-sensitive sensation disappears. SP 9, the he-sea point of the foot taiyin spleen channel, and can fortify the spleen, remove dampness and regulate menstruation.
Treat once a day, using one or two groups of the above acupoints each time. Ten treatments make a treatment course. In total, give three to five courses.
Conclusion
Moxibustion is ability to promote blood circulation, remove dampness and unblock the collaterals making it effective in the treatment of chronic pelvic inflammation. Patients should be advised to keep warm and not wear themselves out before, after, and during menstruation.
Proper hygiene during sexual activity is very important, as is hygiene during the menstrual period, after abortions or miscarriages, and in the weeks after childbirth.




