Lumbar disc herniation involves pathological changes to the intervertebral discs, fracture of the fibrous rings, or prolapse of the nucleus pulposus, which can irritate and compress neighboring tissues such as the nerve root and spinal cord, causing low back pain and unilateral or bilateral numbness. The condition is usually caused by injury, strain or attack by cold. The intervertebral discs between L4-5 and L5-S1 are affected in 90%-96% of cases. Generally, pathology occurs in only one intervertebral disc.
In TCM, Lumbar disc herniation falls under low back pain or pain of the waist and legs. Trauma and strain can lead to blood stasis obstructing the sinews. When there is a blockage, there is pain. Likewise, obstruction can be caused when the channels and collaterals of the low back are attacked by cold damp or damp heat. Third, liver and kidney depletion can lead to poor nourishment of the bones. According to channel and collateral theory, the foot taiyang bladder channel travels through the Jiaji points to the low back, the Du Mai travels through the spinal cord to the low back, and the foot shaoyin kidney channel travels through the low back. This area is said to be governed by the kidney, and is called the house of the kidney. Thus low back pain is connected with disorders of the channels and sinews of the Foot Taiyang Bladder channel, Du Mai, and the Foot Shaoyin Kidney channel.
Clinical manifestations of lumbar disc herniation
- There is often a history of trauma, chronic strain, or exposure to cold-damp.
- Low back pain and discomfort.
- Numbness of and radiating pain to the lower limbs that are aggravated by coughing or sneezing.
9 Acupuncture points for lumbar disc herniation
The basic therapeutic principles are to dispel wind, dissipate cold, invigorate blood, unblock the channels, and dredge and regulate the channel sinews. Distal acupoints on the channels that pass through the affected area are chosen mainly on the Du Mai, Foot Taiyang Bladder Channel, and Foot Shaoyang Gallbladder Channel.
1. GV 9 Acupoint (Zhiyang)
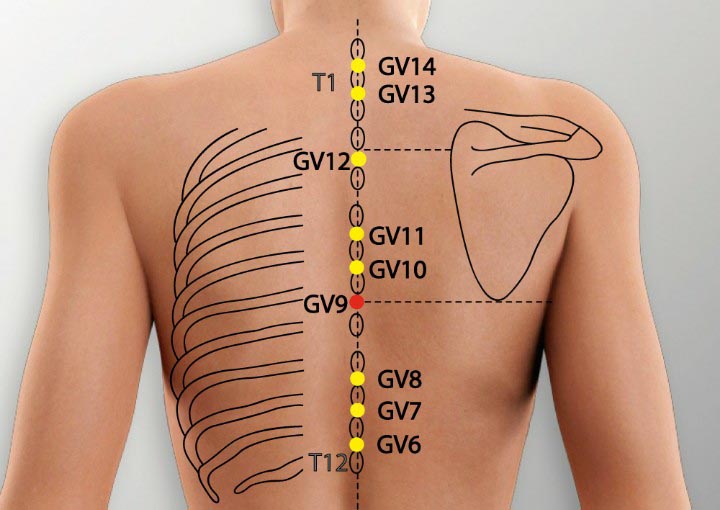
Location: On the posterior midline in the depression below the spinous process of the seventh thoracic vertebra.
Effect: Strengthens the low back and spinal cord, unblocks the collaterals, relieves pain.
2. GV 4 Acupoint (Mingmen)
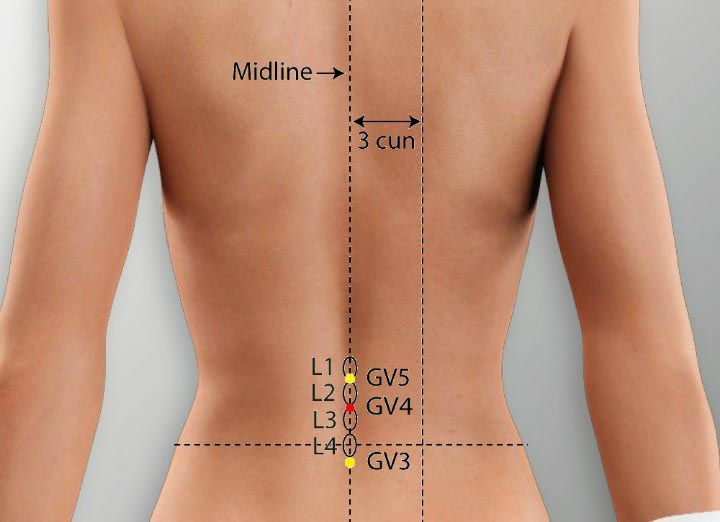
Location: On the lower back on the posterior midline in the depression under spinous process of the second lumbar vertebrae.
Effect: Supplements and boosts kidney qi, strengthening the low back and spinal cord.
3. GV 2 Acupoint (Yaoshu)
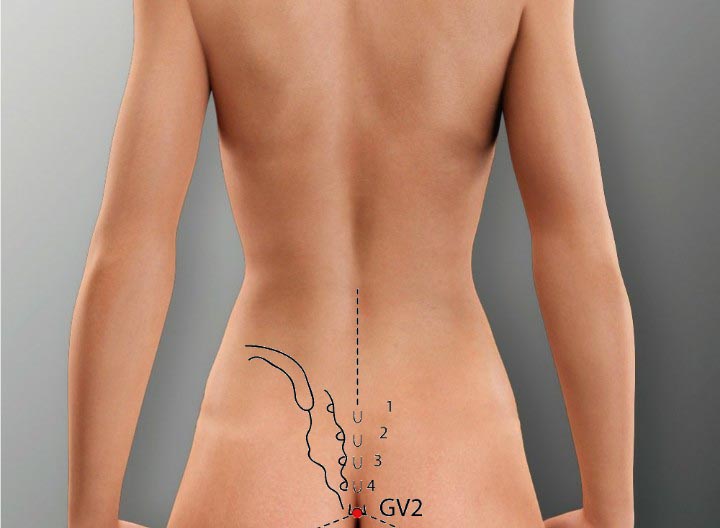
Location: On the back on the posterior midline, at the level of the sacral hiatus.
Effect: Strengthens the low back and spinal cord, unblocks the collaterals, relieves pain.
4. BL 26 Acupoint (Guanyuanshu)
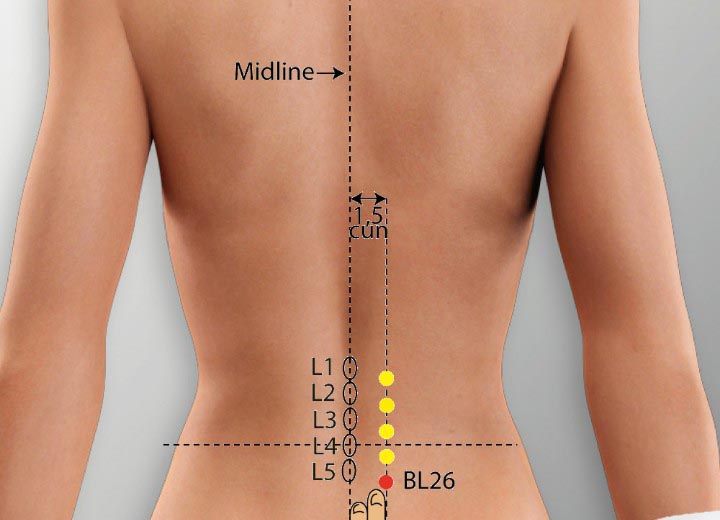
Location: On the low back level with the lower border of the spinous process of the fifth lumbar vertebra, 1.5 cun lateral to the posterior midline.
Effect: Supplements and boosts kidney qi, strengthens the low back and spinal cord.
5. BL 36 Acupoint (Chengfu)
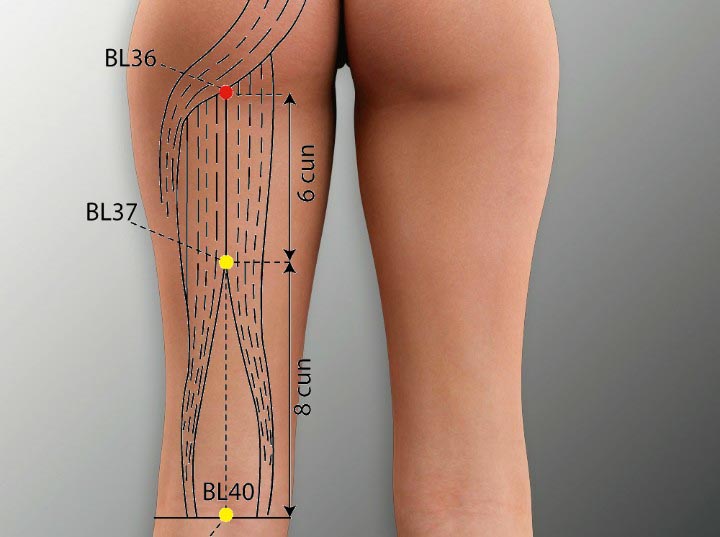
Location: On the posterior thigh, on the midpoint of the transverse gluteal crease.
Effect: Promotes the low back and spinal cord, unblocks the collaterals, and relieves pain.
6. BL 40 Acupoint (Weizhong)
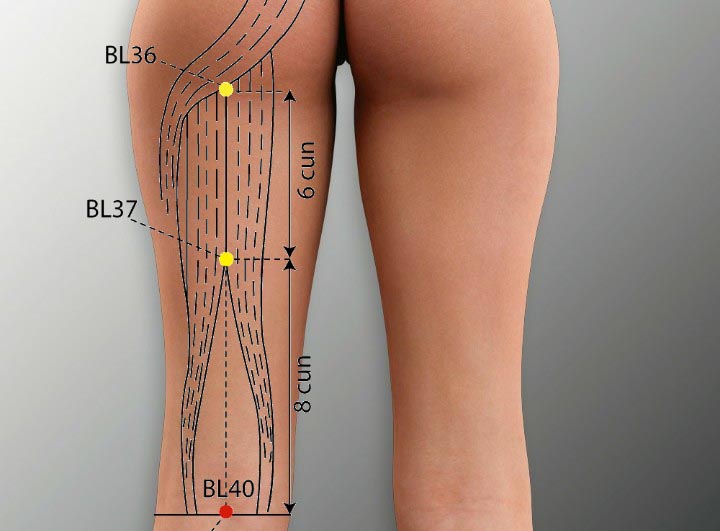
Location: On the midpoint of the popliteal crease, in the middle of the biceps femoris tendon and the semitendinous tendon.
Effect: Unblocks the collaterals, relieves pain, strengthens the low back and spinal cord.
7. BL 60 Acupoint (Kunlun)
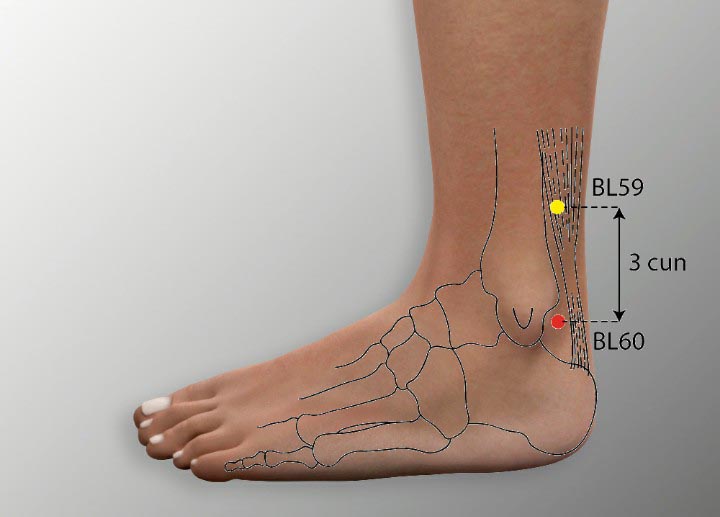
Location: Posterior to the external malleolus in the depression between the malleolus and the achilles tendon.
Effect: Unblocks the channels, quickens the collaterals, relieves pain.
8. GB 34 Acupoint (Yanglingquan)
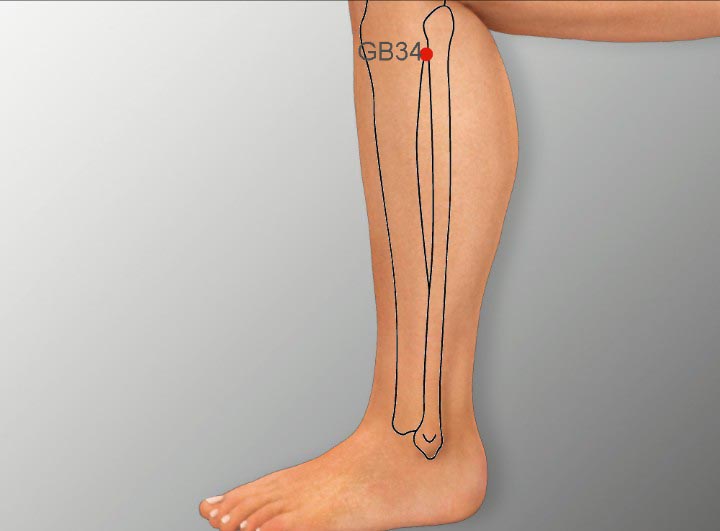
Location: On the lateral side of the lower leg, in the depression anterior-inferior to the head of the fibula.
Effect: Unblocks the collaterals, rectifies qi, relieves pain.
9. Tender points on the low back
Location: On the low back.
Effect: Unblocks the collaterals, relieves pain, dredges the channels of the low back, promotes the function of the spinal cord.
Moxibustion treatment methods
- Relaying and back-and-forth moxibustion in the area of GV 2, GV 4, and GV 9 to promote the yang qi of the Du Mai. The patient should feel heat transmitted along the Du Mai in the lumbosacral region. Located on Du Mai, the combination of GV 2, GV 4, and GV 9 can supplement kidney qi, strengthen the low back and spinal cord, unblock the collaterals, and relieve pain.
- Single-point mild moxibustion on BL 26 on the affected side. The patient should feel the heat penetrate deeply, expand over the area, transmit to the lower limbs, or feel local tightness, pressure, soreness, distention and pain. In some patients, the heat transmission will reach the heel. If it fails to do so, apply relaying moxibustion with another moxa stick on BL 36, BL 40, GB 34, and BL 60 in this order to cause the heat to transmit to the heel. Finally, administer mild moxibustion on BL 60 and BL 26 with two moxa sticks. Stop moxibustion when the heat-sensitive sensation disappears. Located on the Foot Taiyang Bladder channel and the Foot Shaoyang Gallbladder channel,the combination of BL 26, BL 36, BL 40, GB 34, and BL 60 can unblock the channels and collaterals, promote the function of the low back and spinal cord, and relieve pain.
- Single-point mild moxibustion on tender points on the low back. The patient should feel the heat penetrate deeply into the abdominal cavity, expand over the area, transmit to the lower limbs, or feel local tightness, pressure, soreness, distention, and pain.
Treat once a day, choosing one or two groups of the above acupoints each time. Ten treatments make a treatment course. In total, give one or two courses with two to five days in between for rest.
Conclusion
Moxibustion can treat both the acute and recovery stages of lumbar disc herniation through its ability to dredge the channels, move qi, reduce inflammation, ease pain and improve circulation.
In the acute stage, the patient should sleep on a hard bed and get plenty of rest to reduce the stimulation of the protuberance on the nerve root. After the symptoms have improved, the dorsal muscles should be exercised. Mild physical activity should be performed while wearing a back support belt.




