Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) refers to a series of symptoms that include abdominal pain, abdominal distention, and changes in defecation habits and the characteristics of the feces. IBS patients experience changes in gastroenteritic motility or sensitivity of the internal organs. The disease affects the entire digestive tract, including the colon, small intestine, stomach and esophagus.
In TCM, IBS is classified as diarrhea, abdominal pain, constipation and constraint. It is usually due to weakness or dysfunction of the zang-fu organs that is caused by an attack of external pathogens, inappropriate eating habits or emotional disorders. The resulting dysfunction of the transportation and transformation function of the spleen leads to an accumulation of water dampness, and failure of the large intestine to conduct and transmit. This disease is usually located in the intestines and the basic mechanisms are spleen deficiency, liver constraint, and disharmony between the liver and spleen.
Clinical manifestations of IBS
- Abdominal pain, abdominal distension, and diarrhea or constipation, accompanied by symptoms of systemic neurosis.
- The patient usually appears to be in good health, with no emaciation or fever. Physical exams only find abdominal tenderness.
- At least three negative coproculture and fecal occult blood examinations.
5 Acupuncture points for IBS
The basic therapeutic principles for IBS are to soothe the liver and fortify the spleen. Acupoints are chosen based on the following principles: the liver governs the free flow of qi; the spleen governs transportation and transformation; the large and small intestines belong to the stomach.
1. ST 25 Acupoint (Tianshu)
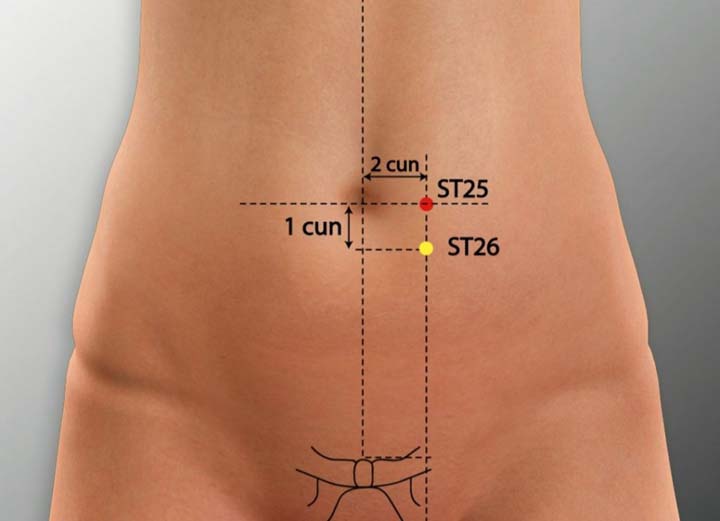
Location: On the abdomen 2 cun lateral to the umbilicus, in the rectus abdominis muscle.
Effect: Regulates the stomach and intestines, rectifies qi, and removes food stagnation.
2. CV 4 Acupoint (Guanyuan)
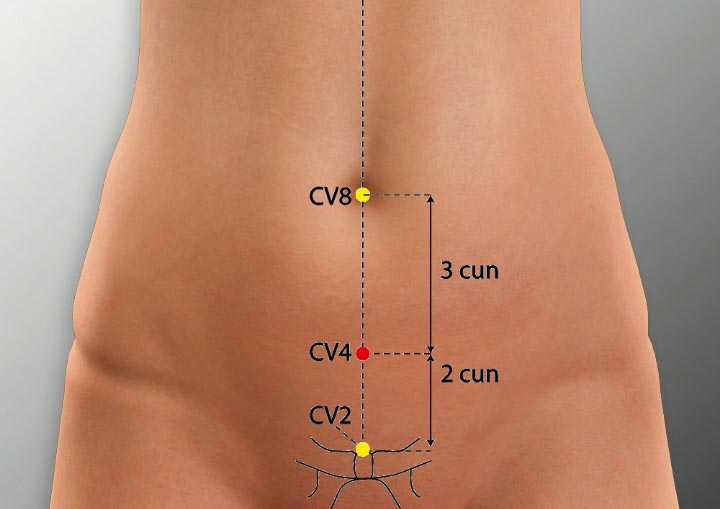
Location: On the lower abdomen on the anterior midline, 3 cun below the umbilicus.
Effect: Supplement original qi, regulates the stomach and intestines.
3. GV 4 Acupoint (Mingmen)
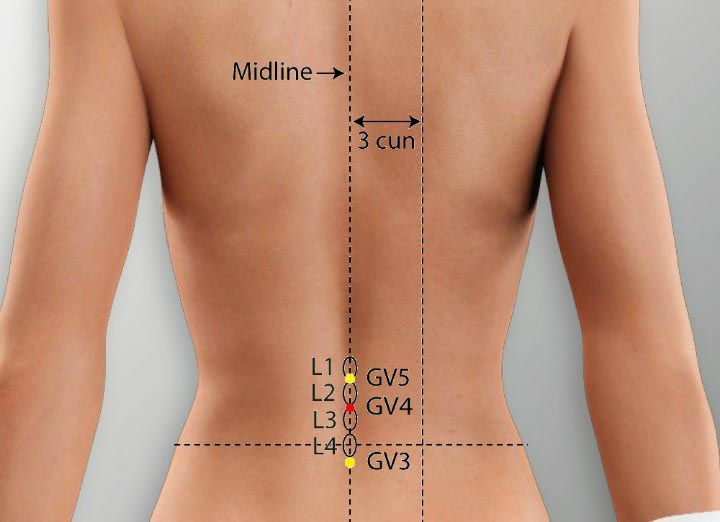
Location: On the lower back on the posterior midline in the depression under the spinous process of the second lumbar vertebrae.
Effect: Supplements of kidney qi, regulate the stomach and intestines.
4. BL 25 Acupoint (Dachangshu)
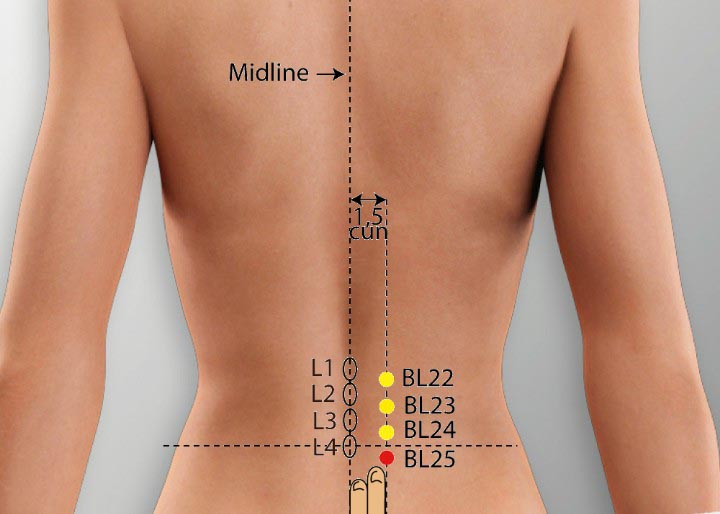
Location: On the lower back 1.5 cun lateral to the posterior midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the fourth lumbar vertebrae.
Effect: Rectifies qi, dredges the bowels, and regulates the stomach and intestines.
5. ST 36 Acupoint (Zusanli)
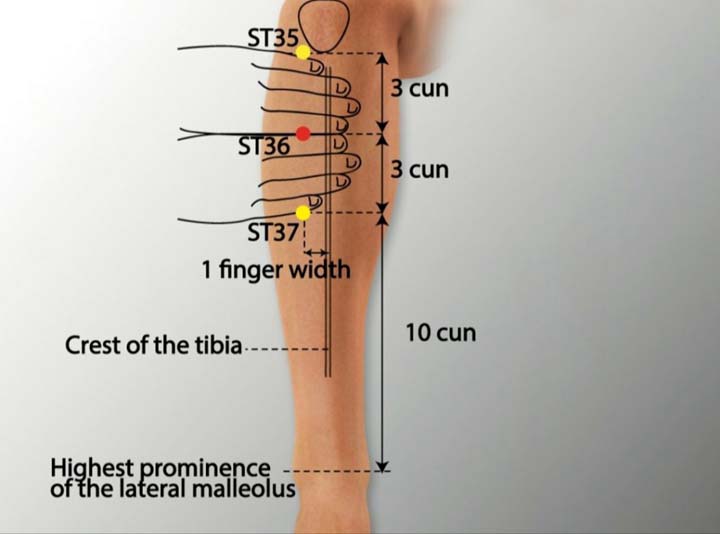
Location: On the anterior-lateral lower leg 3 cun below ST 35, one finger breadth lateral to the anterior border of the tibia, in the tibialis anterior.
Effect: Regulates the stomach and intestines, loosens the intestines, rectifies qi.
Moxibustion treatment methods
- Mild moxibustion on CV 4 and ST 25. The patient should feel heat flow into the abdominal cavity or along the sides to the lower back. The combination of CV 4 and ST 25 can regulate the stomach and intestines, rectify qi, and disperse stagnation.
- Mild moxibustion on BL 25 and GV 4. The patient should feel the heat penetrate into the abdominal cavity, or transmit to the lumbosacral area or the lower limbs. The combination of BL 25 and GV 4 can supplement the kidney, dredge the bowels, and regulate the stomach and the intestines.
- Double-point mild moxibustion on ST 36. The heat transmission sometimes reaches the abdomen. If this does not occur, administer relaying moxibustion with another moxa stick on the most proximal point the heat has to reach to induce it to arrive at the abdomen. Finally, administer mild moxibustion using two moxa sticks on ST 36 and the abdomen until the heat-sensitive sensation disappears. ST 36 is the he-sea point of the foot yangming stomach channel, and can regulate the stomach and intestines, loosen the intestines and rectify qi.
Choose one or two groups of the above acupoints and treat once a day.Ten treatments make a course. Two or three courses should be given in total with a break of two to five days between courses.
Conclusion
Moxibustion can effectively treat IBS, and is recommended as the first choice for treating this disease.
Patients should get plenty of physical exercises to strengthen their bodies. They should maintain balanced moods and get enough sleep. They should eat frequent, small meals, and avoid irritating food and food that is too cold or hot. They should not smoke, drink much alcohol, and avoid wind and cold.