Chronic prostatitis is an inflammatory disease caused by a non-specific infection of the prostate tissue, which presents as irritation of the urinary tract, urinary difficulty, and heaviness and distending pain of the perineum. Urinary tract irritation may manifest as frequent, urgent or painful urination. The disease is mostly seen in young men. It develops slowly, has complex symptoms, has a prolonged course, is difficult to cure and tends to recur.
In TCM, chronic bacterial prostatitis falls under white turbidity and strangury due to overwork. Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis falls under chylous strangury and essence turbidity. TCM links this disease to unsatisfied libido, excessive sexual activity, stirring of ministerial fire, excessive alcohol intake, fatigue, damp-heat pouring downwards, and obstruction by vanquished semen.
Clinical manifestations of chronic prostatitis
- The symptoms fall under two types: irritation of the lower urinary tract, and inflammatory reactions or reflex pain. The manifestations include urinary frequency, urgency and pain, vesical tenesmus, and a burning urethra. There can also be a discharge of a small amount of white secretions from the urinary tract when getting up in the morning and at the end of urination or defecation. Heavy distending pain can occur in the perineum, external genitalia, lower abdomen, suprapubic region, waist, sacral region, and around the anus.
- Palpation of the prostate reveals swelling, irregular texture, inflammatory nodes, or a tough texture. There can be tenderness, and its shape can be normal, larger, or smaller than normal.
- WBC≥10/HP and below-normal levels or absence of lecithin.
The presence of any of the above can confirm the diagnosis of chronic prostatitis.
5 Acupuncture points for chronic prostatitis
The basic therapeutic principles are to clear heat, drain dampness, rectify qi and invigorate blood. Relevant acupoints are chosen based on the following principles: the kidney governs reproduction; the pathways of Ren Mai, Du Mai and the foot jueyin liver channel pass through the groin.
1. CV 4 Acupoint (Guanyuan)
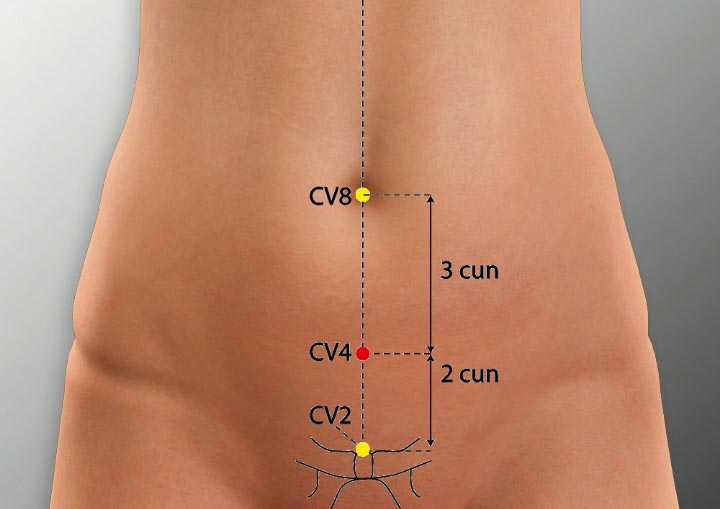
Location: On the lower abdomen on the anterior midline, 3 cun below the umbilicus.
Effect: Supplements original qi, transforms qi, promote urination.
2. CV 3 Acupoint (Zhongji)
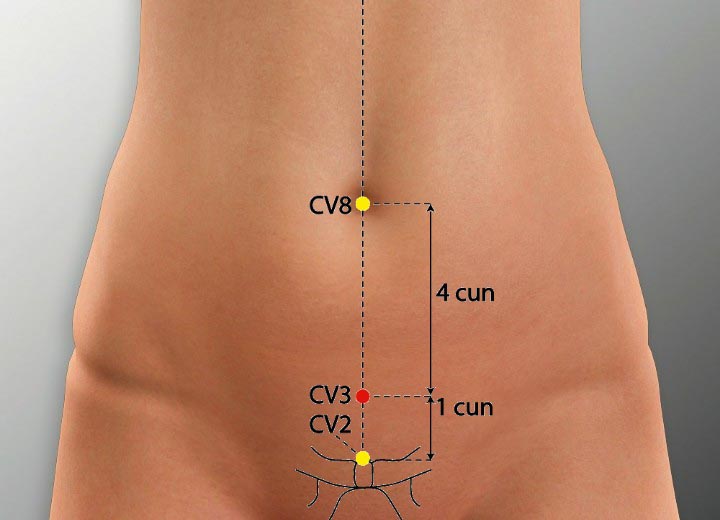
Location: On the lower abdomen on the anterior midline, 4 cun below the umbilicus.
Effect: Supplements the kidney, boosts qi, frees and regulates the waterways.
3. BL 23 Acupoint (Shenshu)
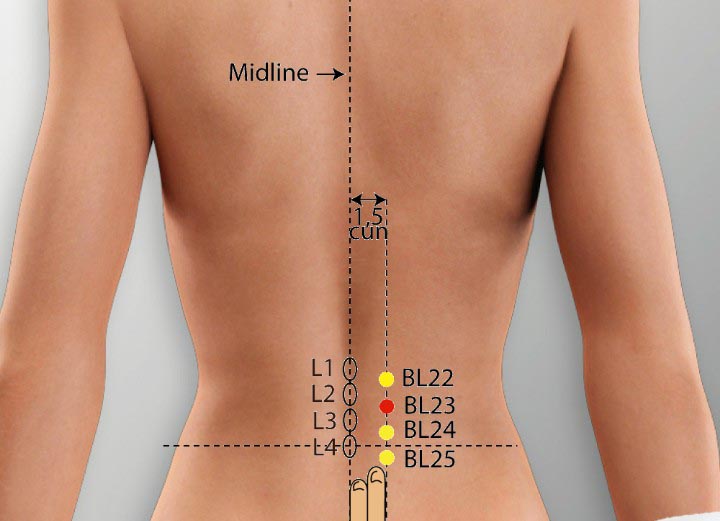
Location: On the low back, below the spinous process of the second lumbar vertebra, 1.5 cun lateral to the posterior midline.
Effect: Strengthens the low back and spine, supplements yin and yang.
4. GV 4 Acupoint (Mingmen)
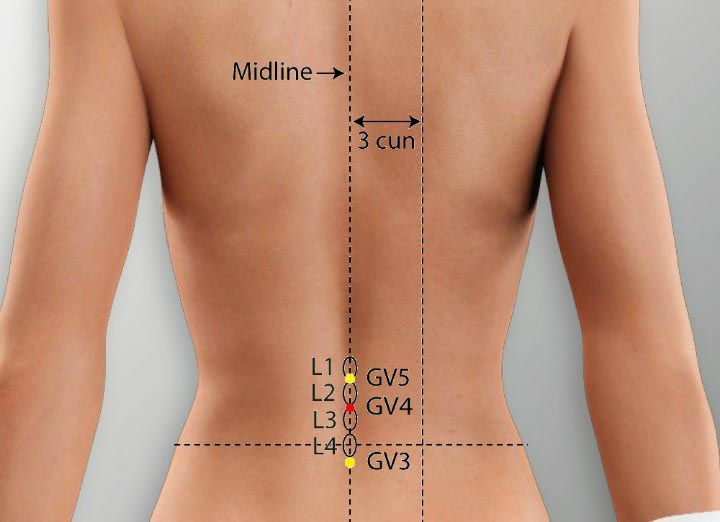
Location: On the lower back on the posterior midline in the depression under the spinous process of the second lumbar vertebrae.
Effect: Supplements and boosts original qi.
5. BL 32 Acupoint (Ciliao)
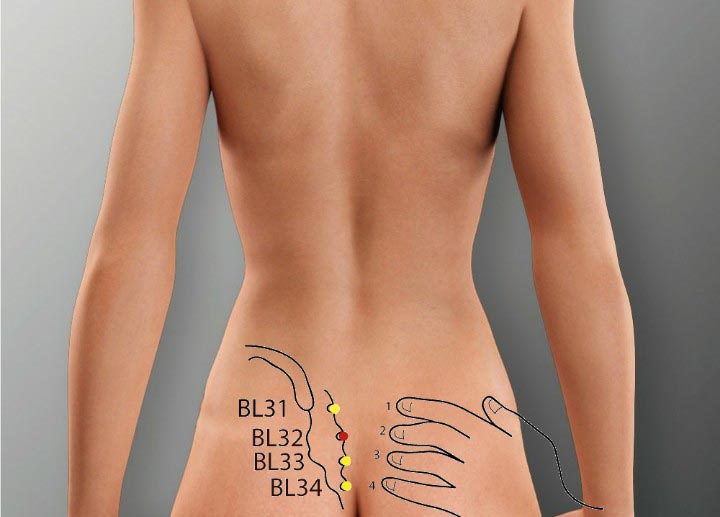
Location: On the medial-inferior side of the posterior inferior iliac spine, over the second posterior sacral foramina.
Effect: Unblocks the collaterals, relieves pain, and promotes urination.
Moxibustion treatment methods
- Double-point mild moxibustion on CV 4 and CV 3. The patient should feel the heat penetrating deep into the abdominal cavity and transmitting along the Dai Mai to the lumbosacral region. Located on the Ren Mai, the combination of CV 4 and CV 3 can supplement the original qi, and free and regulate the waterways.
- Double-point mild moxibustion on BL 23. The patient should feel heat penetrating and expanding over the waist and lower back, and then transmitted to the lower abdomen. BL 23 is where the qi and blood of the kidney gather at the back, and thus can strengthen the low back, supplement the kidney, and supplement yin and yang.
- Mild moxibustion on GV 4 and BL 32. The patient should feel heat penetrating and expanding over the waist and lower back, and then transmitted to the lower abdomen. The combination of GV 4 and BL 32 can supplement and boost original qi, unblock the collaterals, relieve pain, and promote urination.
Treat once a day, choosing one or two groups of the above acupoints. Ten treatments make a treatment course. Give two or three courses total, with two to five days in between for rest.
Conclusion
Western medical treatments of chronic prostatitis are not satisfactory. Moxibustion can regulate the immune system, has anti-inflammatory effects, and can improve local blood circulation to improve chronic prostatitis.
Patients should keep warm, stay away from alcohol, limit sexual activity and maintain a proper work-rest balance.