With a history of nearly 3,000 years, Traditional Chinese Medicine(TCM) has formed a unique system to diagnose and cure diseases. The TCM approach is fundamentally different from that of Western […]


With a history of nearly 3,000 years, Traditional Chinese Medicine(TCM) has formed a unique system to diagnose and cure diseases. The TCM approach is fundamentally different from that of Western […]
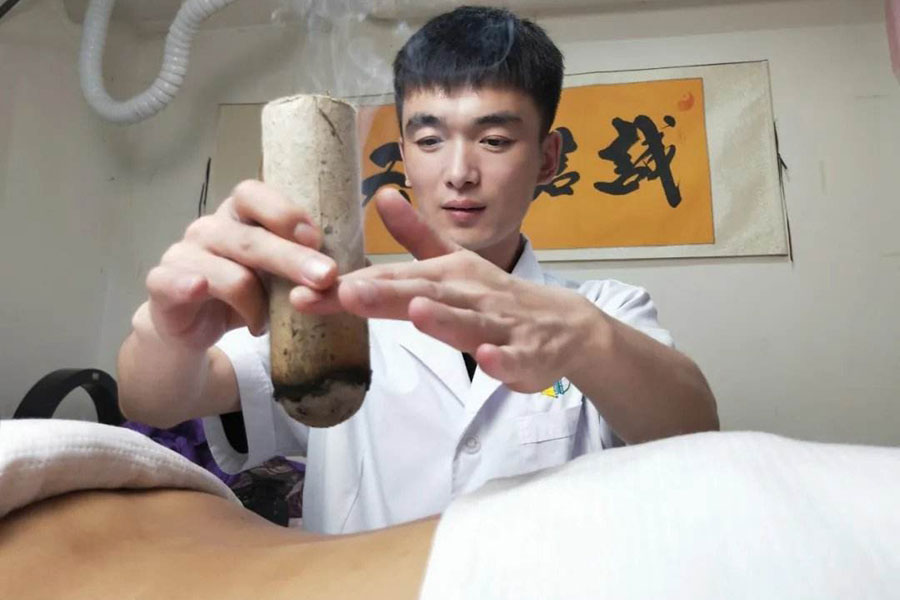
Low back pain is one of the most common conditions in the adult population. It is estimated that more than 80% of the population will suffer from it at some […]

Moxibustion effect on trigeminal neuralgia is due to its ability to unblock the collaterals and relieve pain. However, a complete cure is often difficult to achieve. Patients should be optimistic and avoid becoming irritable or worried.
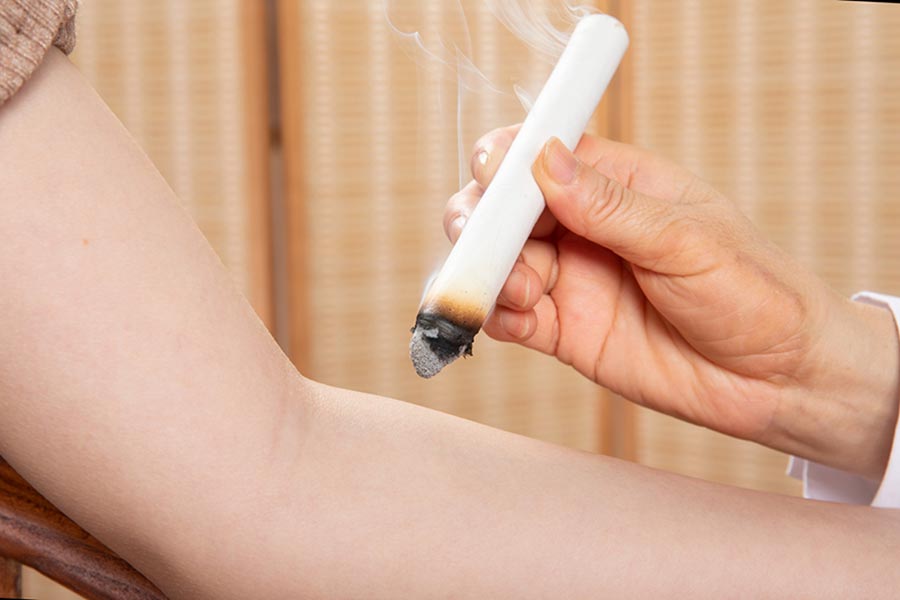
Moxibustion is able to diminish inflammation and ease the pain. After recovery, patients should avoid wind, cold, and overstrain.
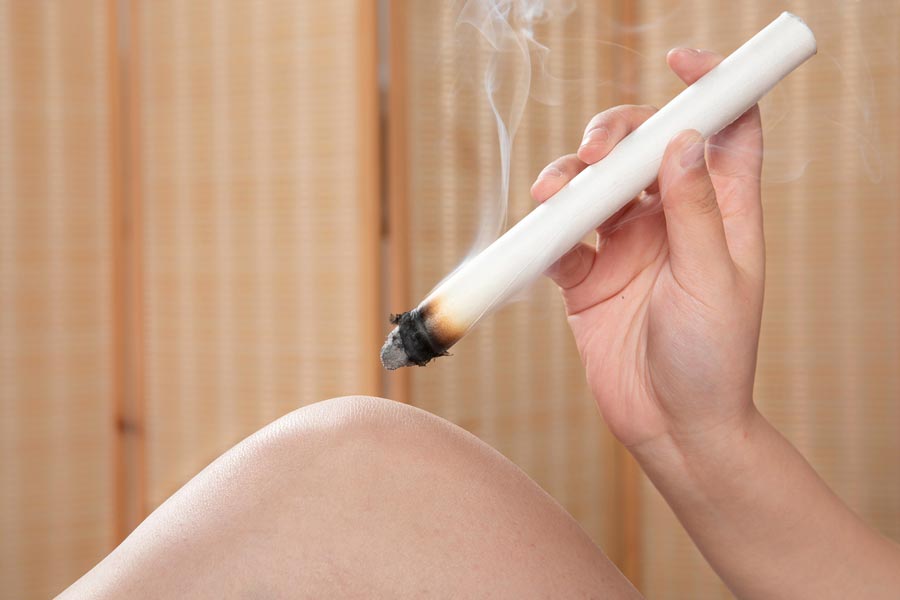

Moxibustion treats knee osteoarthritis through its ability to dredge the channels, move qi, reduce inflammation, ease pain and improve circulation.
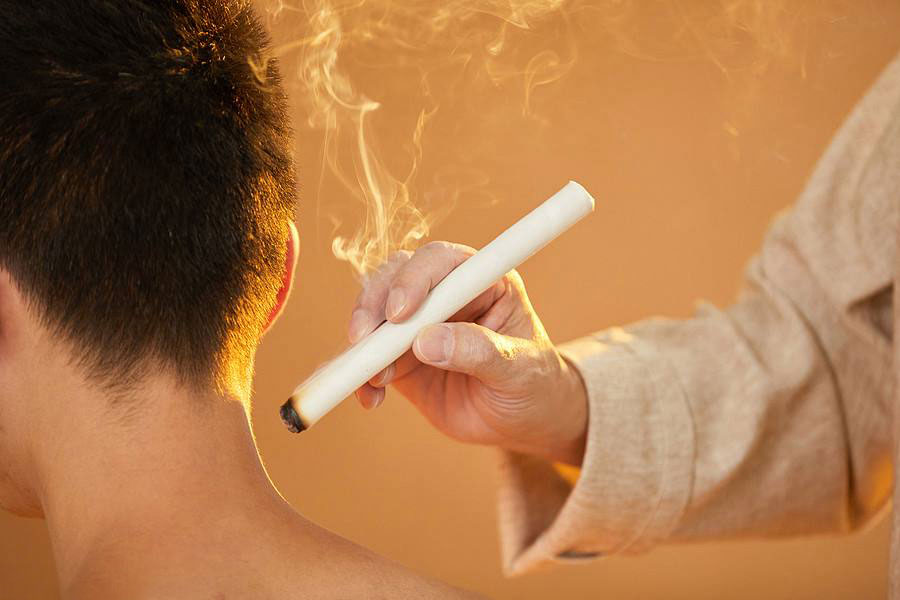

Moxibustion can effectively treat myofascial pain, and early diagnosis and intervention improve the effect. If there are indurations in the muscle, the course of treatment will be longer.
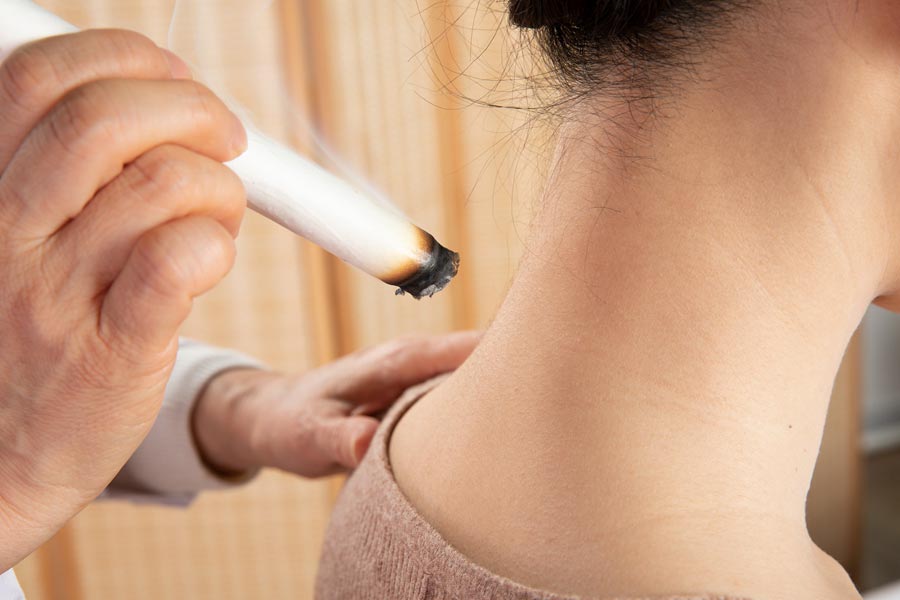
Moxibustion can treat frozen shoulder through its ability to dredge the channels and unblock the collaterals, which reduce inflammation and ease the pain.
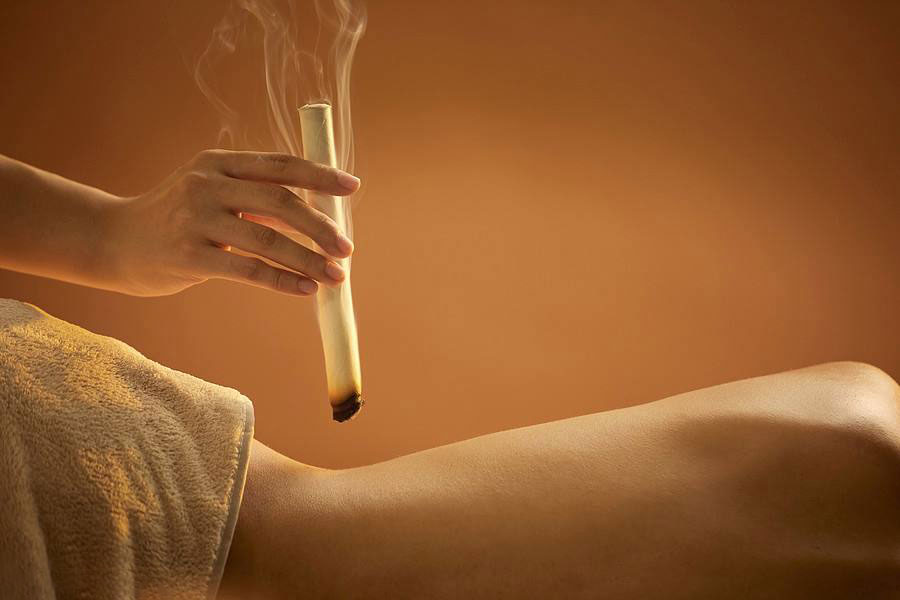

Moxibustion can treat both the acute and recovery stages of lumbar disc herniation through its ability to dredge the channels, move qi, reduce inflammation, ease pain and improve circulation.

Moxibustion treats Cervical spondylosis by dispelling cold, removing dampness, and warming and unblocking the channels.
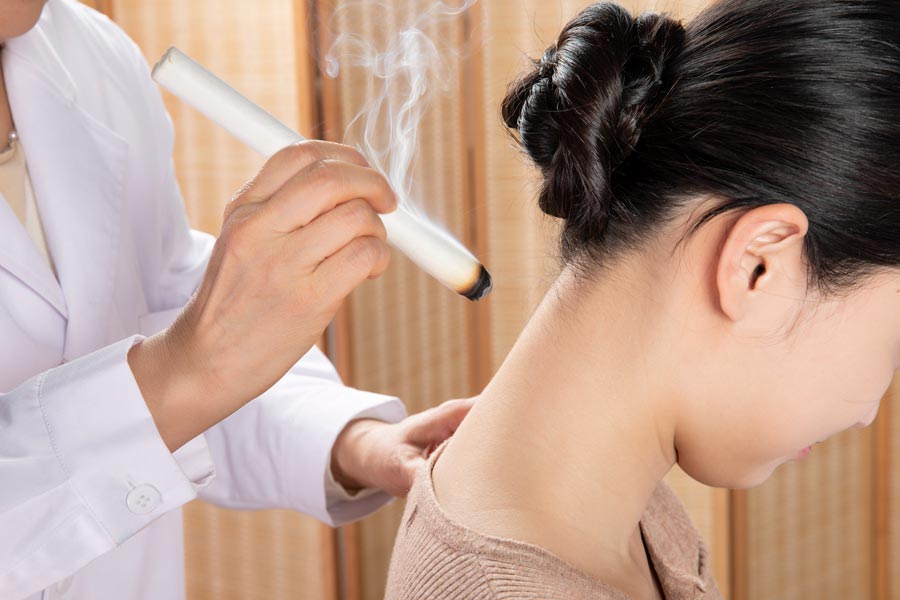

Moxibustion can warm yang, free the flow of qi, and enhance immunity, and is thus effective in the treatment of allergic rhinitis.